KiMMI-SF
Adaptive software framework for context-sensitive, intuitive man-machine-interaction

The aim of project "KiMMI SF" is the development of a software framework for flexible and context-optimized man-machine-interaction. On the one hand, this shall offer online reconfigurable data handling. Furthermore, methods for context-dependent evaluation, selection and weighting of data sources will be developed.
Project details
KiMMI SF is a joint research project with the aim of realizing a software framework for flexible human-machine interaction which is optimal for the respective context.
Specifically, in subproject 1 “Development of an adaptive software framework for MMI”, led by DFKI RIC, an adaptive software framework is being developed that enables online reconfigurable data processing based on different data sources. The framework shall enable a multimodal evaluation of the situation of the human being, the agent and the environment.
In subproject 2 “Development of methods for online context recognition”, led by the University of Bremen, methods for context-dependent evaluation, selection and weighting of data soures will be developed to enable online interpretation of context information based on multimodal data and to derive the human condition. The software framework developed in the project is a prerequisite for context-dependent intuitive human-machine interaction, which is to be made possible through collaboration in the project. This will allow the interaction between humans and robotic agents to continue flexibly, i.e. even when the context changes.
Due to the adaptive nature of the software framework to be developed in KiMMI SF for flexible human-machine interaction that is optimal for the respective context, it is expected, among other things, that downtimes due to otherwise unrecognized context and intention changes in humans can be minimized. Thus, it can serve as an essential contribution for the success of future missions. KiMMI SF builds on existing technology developments in previous projects in the field of space travel, particularly in the area of providing services (PS).
Videos
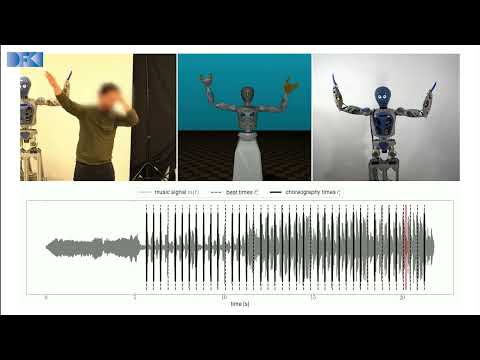
RH5 Manus: Robot Dance Generation based on Music Analysis Driven Trajectory Optimization

Musical dancing is an ubiquitous phenomenon in human society. Providing robots the ability to dance has the potential to make the human robot co-existence more acceptable. Hence, dancing robots have generated a considerable research interest in the recent years. In this paper, we present a novel formalization of robot dancing as planning and control of optimally timed actions based on beat timings and additional features extracted from the music. We showcase the use of this formulation in three different variations: with input of a human expert choreography, imitation of a predefined choreography, and automated generation of a novel choreography. Our method has been validated on four different musical pieces, both in simulation and on a real robot, using the upper-body humanoid robot RH5 Manus.
RH5 Manus: Background of robot dance generation based on music analysis driven trajectory optimization